Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Identification of Aldehydes and Ketones by NaHSO3, Condensation-Elimination Reactions of Aldehyde and Ketones, Popoff's Rule for Oxidation of Ketones, Cross Cannizzaro's Reaction, etc.
Important Questions on Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
Compound which gives cannizzaro reaction?
Given reaction is an example of
Given reaction is an example of
Oxidation number of carbon changes from
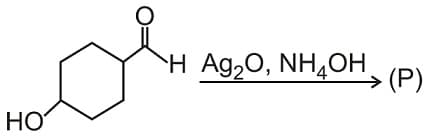
Product (P) is
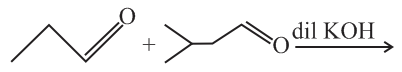
Total number of aldol condensation products are (excluding stereoisomer)
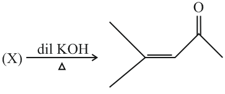
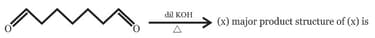
Structure of is:
Aldol addition can be
Aldol addition can be
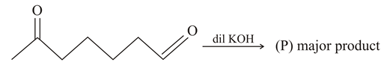
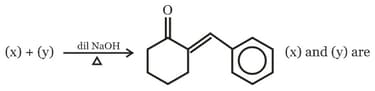
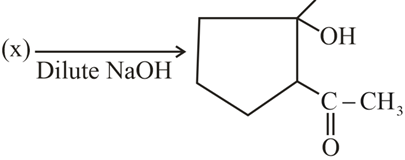 ; (X) is
; (X) is
The Tollen’s regent is:
Reduction of the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with potassium hydroxide is known as
Name the following reactions:
The carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketones is reduced to group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Aldehydes that do not contain any hydrogen atom undergo self-oxidation and reduction reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali.
The chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds are:
() Propanal and propanone
() Acetophenone and benzophenone
Write the name of following chemical reactions.
(i) Aldehydes which do not contain an hydrogen atom, when treated with a concentrated alkali solution undergo self-oxidation–reduction.
(ii) Carboxylic acids react with chlorine or bromine in the presence of phosphorous to give compounds in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by a halogen atom.
The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by which of the following test:
(i) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(ii) Ethanal and Propanal
The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by which of the following test:
(i) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(ii) Ethanal and Propanal